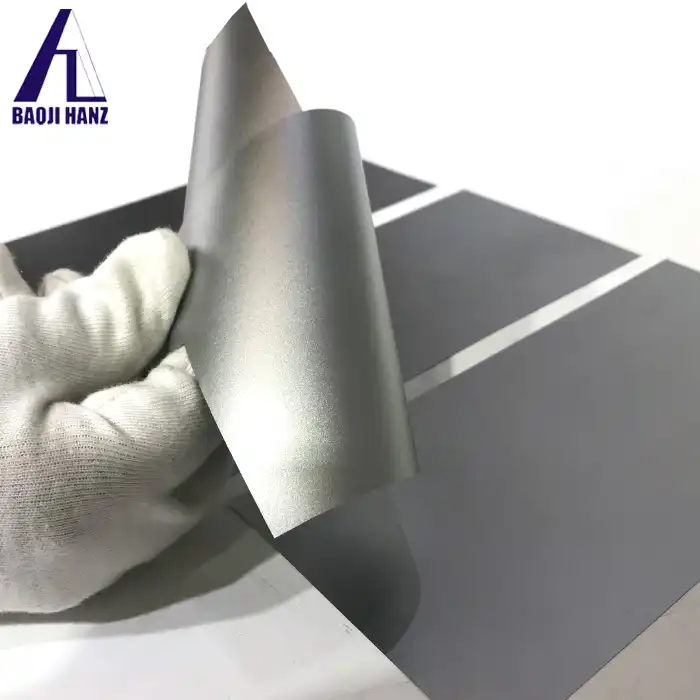
Are nitinol sheets flexible?
2024-07-16 15:55:22
What Makes Nitinol Sheets Flexible?
Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium, stands out due to its superelasticity and shape memory effect. These characteristics enable Nitinol sheets to undergo significant deformation and return to their original shape. The flexibility of Nitinol Metal Sheets arises from their ability to absorb and release mechanical energy efficiently.
Superelasticity and Shape Memory Effect
Superelasticity allows Nitinol sheets to bend and twist significantly without permanent deformation. When stress is applied, the sheets transform their crystal structure from austenite to martensite, enabling them to flex. Upon removing the stress, they revert to their original structure, regaining their initial shape.
The shape memory effect further enhances flexibility. When Nitinol Alloy Sheets are deformed at a lower temperature, they can return to their pre-deformed shape upon heating. This property is particularly useful in applications requiring precise control of shape changes, such as medical stents and actuators.
How Are Nitinol Sheets Manufactured?
The manufacturing process of Nitinol sheets is intricate, involving several stages to ensure optimal properties. It typically includes melting, casting, rolling, and annealing.
Melting and Casting
The process begins with melting nickel and titanium in a vacuum or inert atmosphere to prevent contamination. The molten alloy is then cast into ingots, which are subsequently hot-rolled to reduce thickness and improve mechanical properties.
Rolling and Annealing
Hot rolling transforms the ingots into thinner sheets. This step is followed by annealing, where the sheets are heated to a specific temperature and then cooled at a controlled rate. Annealing relieves internal stresses and refines the microstructure, enhancing the flexibility and durability of the Nitinol Metal Sheets.
What Are the Applications of Flexible Nitinol Sheets?
Nitinol sheets' unique properties make them suitable for a wide range of applications across various industries.
Medical Devices
In the medical field, Nitinol Alloy Sheets are used in stents, guidewires, and orthodontic archwires. Their flexibility and biocompatibility ensure they can navigate through complex bodily structures without causing damage. The shape memory effect is particularly beneficial for stents, which can be compressed for insertion and then expand to their intended shape within the body.
Aerospace and Robotics
Nitinol sheets are also pivotal in aerospace and robotics. Their ability to withstand extreme conditions and return to their original shape makes them ideal for actuators and sensors. In robotics, Nitinol Alloy Sheets are used in soft robotics, where flexibility and resilience are crucial for mimicking natural movements.
Consumer Electronics
The consumer electronics industry leverages the properties of Nitinol Metal Sheets in foldable devices and connectors. The flexibility and durability of Nitinol enhance the performance and longevity of these products, ensuring they can withstand repeated bending and twisting.
Are Nitinol Sheets Corrosion-Resistant?
Corrosion resistance is a critical factor for materials used in harsh environments. Nitinol sheets exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for various applications.
Surface Oxide Layer
Nitinol sheets develop a thin oxide layer on their surface, primarily composed of titanium oxide. This layer acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying material from corrosive elements. The presence of nickel also contributes to the overall corrosion resistance.
Corrosion Performance in Different Environments
Studies have shown that Nitinol Alloy Sheets perform well in both acidic and alkaline environments. Their corrosion resistance is comparable to that of stainless steel, making them a reliable choice for applications in marine, medical, and chemical industries.
How Do Nitinol Sheets Compare to Other Flexible Materials?
When compared to other flexible materials, Nitinol sheets offer several distinct advantages.
Mechanical Properties
Nitinol sheets excel in terms of superelasticity and shape memory effect. While other materials, such as polymers, can also be flexible, they do not exhibit the same level of mechanical strength and resilience. The ability of Nitinol Metal Sheets to undergo large deformations and return to their original shape without fatigue is unparalleled.
Temperature Range
Nitinol Alloy Sheets can operate over a wide temperature range, maintaining their properties even in extreme conditions. This contrasts with other flexible materials, which may lose flexibility or degrade at high temperatures.
Biocompatibility
In medical applications, the biocompatibility of Nitinol sheets is a significant advantage over other materials. Polymers and other metals may cause adverse reactions within the body, whereas Nitinol is well-tolerated and integrates seamlessly with biological tissues.
Conclusion
Nitinol sheets are a remarkable material with unparalleled flexibility, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. Their superelasticity and shape memory effect enable them to be used in diverse applications, from medical devices to aerospace components. The manufacturing process ensures these properties are optimized, making Nitinol Alloy Sheets a preferred choice in various industries.
References
- Title: Superelasticity and Shape Memory Effect in Nitinol, Journal of Materials Science
- Title: Manufacturing Processes of Nitinol Alloys, International Journal of Metallurgy
- Title: Biocompatibility of Nitinol in Medical Applications, Biomedical Engineering Journal
- Title: Corrosion Resistance of Nitinol Alloys, Corrosion Science
- Title: Applications of Nitinol in Aerospace Engineering, Aerospace Materials Journal
- Title: Nitinol in Consumer Electronics, Electronics Materials Review
- Title: Surface Oxide Layers in Nitinol, Surface Science Reports
- Title: Comparison of Flexible Materials: Nitinol vs. Polymers, Materials Science Review
- Title: Performance of Nitinol in Acidic and Alkaline Environments, Chemical Engineering Journal
- Title: Nitinol Actuators and Sensors in Robotics, Robotics and Automation Journal