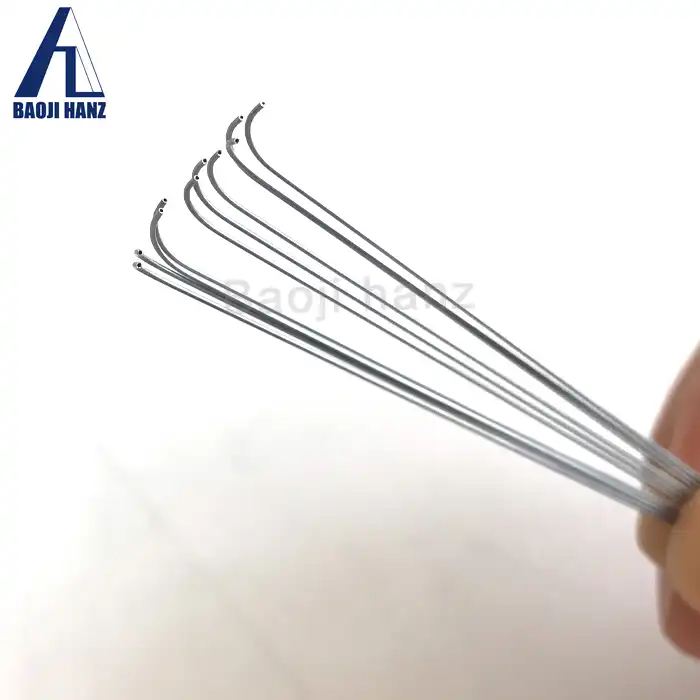
Medical nitinol tube
| Product name | Niti tube for medical use |
| Material | nitinol medical grade |
| Chemical | nickel 54-57% titanium balance |
| Af | 0-20 degree |
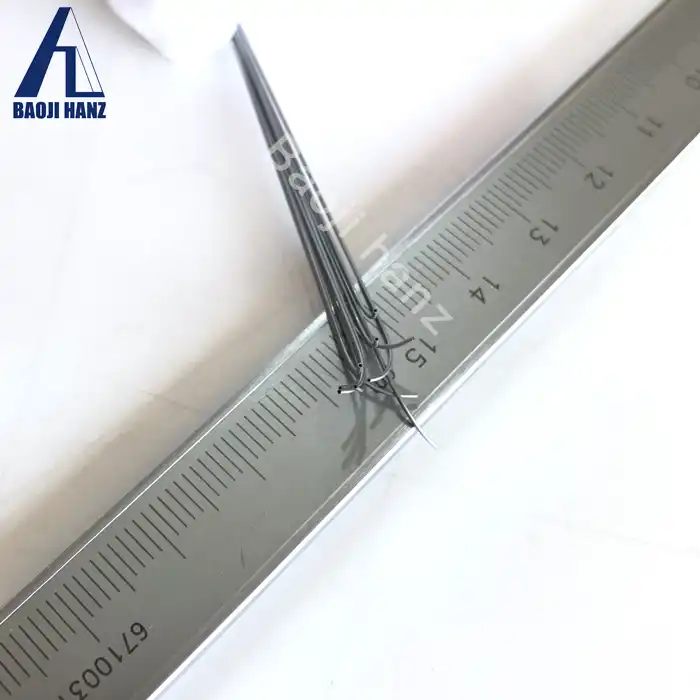
| Diameter | OD from 0.1mm min , thickness from 0.035mm min, length no specified |
| MOQ | 5 meters |
| Surface | outside centerless grinding, inside no oxided , no oil |
| Standard | ASTM F2633 |
| Application | medical, produce medical device, making nitinol stent, used as medical cathetor and so on |
Nickel-titanium tubes, leveraging their shape memory effect, superelasticity, excellent biocompatibility, and corrosion resistance, have become core materials in medical applications such as minimally invasive interventions and tissue repair. They are widely used across various specialized fields, including cardiovascular, digestive, urological, orthopedic, neurointerventional, and dental disciplines, and are often tailored to meet the demands of precision and minimally invasive clinical practices.
1. cardiovascular field,
Coronary artery stent: One of the most classic medical applications of nitinol tubes. The tube is compressed to a fine diameter and implanted into the narrowed vascular area via a catheter. At the human body temperature of 37°C, it automatically expands to its preset diameter, supporting the vessel wall. Its superelasticity allows it to adapt to vascular pulsations, preventing stent compression and reducing the risk of restenosis. Additionally, it resists bodily fluid corrosion and has a long service life.
Cardiac Interventional Catheter/Wire Sheath: Used for interventional procedures such as arrhythmias and heart valve diseases. Fine-diameter 0.7mm nickel-titanium tubes can navigate tortuous cardiac vessels. Their superelasticity prevents intraoperative stalling, bending, and vascular damage. Additionally, the pre-shaped design enables precise targeting of lesions, enhancing surgical efficiency.
Peripheral vascular stents: For peripheral vascular stenosis such as lower limb arteries and renal arteries, nitinol stents can withstand repeated compression during limb movement and maintain vascular patency over the long term. Compared to traditional metallic stents, they reduce the risk of stent deformation and failure caused by limb motion.
2. Digestive field
Biliary/Pancreatic Stents: Designed for use in narrow sections of the intrahepatic bile ducts and pancreatic ducts, particularly in fine ductal lumens with diameters <3mm. The nitinol tube can be compressed to a minimal size for endoscopic implantation and expands stably to maintain patency after deployment. Resistant to bile and pancreatic fluid corrosion, it has a service life exceeding 12 months, far surpassing traditional plastic stents (which last only 3-6 months).
Esophageal/Gastrointestinal Stents: Used for the dilation treatment of postoperative stenosis or obstruction in esophageal cancer and gastric cancer, as well as benign esophageal strictures. The superelasticity of nitinol stents allows them to conform to the gastrointestinal tract wall, adapt to gastrointestinal peristalsis, reduce mucosal irritation, and prevent stent displacement, thereby alleviating symptoms such as dysphagia in patients.

3. Urology field
Ureteral stents: Available in adult and pediatric sizes, the pediatric version commonly uses a 0.7mm thin-diameter nitinol tube, designed to fit the narrowed ureteral lumen in children. The stent can deform repeatedly with ureteral peristalsis, preventing obstruction and mucosal abrasion. This reduces postoperative complications such as hematuria and pain, while offering excellent biocompatibility to avoid rejection reactions with long-term implantation.
Urethral stent: Used for urinary difficulties caused by urethral strictures or benign prostatic hyperplasia. The flexibility of the nitinol tube conforms to the natural curvature of the urethra, while its superelasticity ensures the stent remains patent during urination, reducing pressure on the urethral sphincter and improving patient comfort.
4. Neurointerventional field
Cerebrovascular Microstent: Designed for scenarios such as intracranial microvascular stenosis (diameter <2mm) and aneurysm embolization assistance. The fine-diameter medical nitinol tube can navigate tortuous intracranial vessels, with a pre-shaped design to precisely conform to vascular pathways. Its superelasticity accommodates cerebrovascular pulsations, preventing stent compression of brain tissue vessels and reducing ischemic risk.
Neurointerventional microcatheters: Used in surgeries such as intracerebral hemorrhage and brain tumors, these catheters combine the high strength and flexibility of nitinol tubes, enabling flexible navigation through confined intracranial spaces. They protect neural tissues while providing a stable pathway for surgical instruments, minimizing surgical trauma.

Professional nickel titanium tube solution - Contact us now to customize your exclusive needs
Whether you are a medical device manufacturer, precision industrial enterprise, or a smart wearable device research and development team, our nickel titanium tubes (including full specification precision pipes such as 0.7mm) can accurately adapt to your scene needs. With medical grade qualifications, full scenario customization capabilities, and comprehensive pre-sales and after-sales support, we provide you with one-stop service from sample testing to bulk delivery. Contact now to enjoy exclusive technical solutions and discounted quotes!









_1753930177984.webp)
.webp)

_1764213023283.webp)
_1762931684558.jpg)
